Clinical Case Detail
Return to Clinical Case List
CPC Case # 1
Provided By
Elizabeth Andrews DDS, MS - 2010-05-12
Clinical History
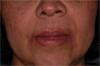
- 50 Year old female
- No significant health history
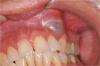
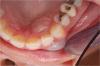
- Reports using a toothpick between teeth #'s 10 & 11 and swelling occurred
- Tooth # 10 is vital and responds to cold
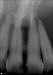
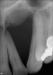
Differential Diagnosis
OKC
Odontogenic Tumor
Intraosseous Salivary Gland Neoplasm
Metastatic tumor
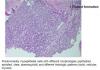
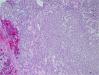
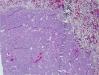
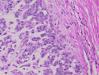
Diagnosis
Myoepithelioma
IHC - S100 protein, cytokeratin, GFAP and alpha smooth muscle actin (SMA) positive
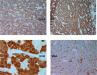
Discussion
DX Intraosseous SGT = 4 Main Criteria
* No pre-existing or concurrent primary SGT
* Origin of tumor from submucosal glands of palate or maxillary antrum or derivation from a primary antral tumor must be excluded
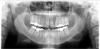
* Cortical bone integrity around tumor proved by imaging technique
* Histologic confirmation of salivary gland tumor
Myoepithelioma Demographics
* 30-90 yo (median 53)
* M=F
* Rare ~1.5% of all tumors of major & minor SG's
* Intraosseous extremely rare - search of Lit 7 cases reported
* Variant of Pleomorphic Adenoma
* Difference is lack of ductal elements <5-10% ducts
* Occasionally undergoes malignant transformation
References
* Regezi, Joseph A., Oral Pathology: Clinical Pathologic Correlations, 5th Edition. Saunders Book Company, 10-2007
* Intraosseous myoepithelioma of the maxilla: clinicopathologic features and therapeutic considerations. Cuesta Gil M, et al. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008 Apr;66(4):800-3
* Intraosseous myoepithelial neoplasms of the maxilla: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations in 5 South African patients. Ferretti C, et al. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003 Mar;61(3):379-86
