CPC Case II
Provided By: Dr. Elizabeth Andrews - 2011-05-18
Clinical History
A 32 year old Hispanic female presents with a chief complaint of red gums. She noticed this after beginning use of whitening strips 6 months ago. Another dentist gave her peridex and this made it worse.
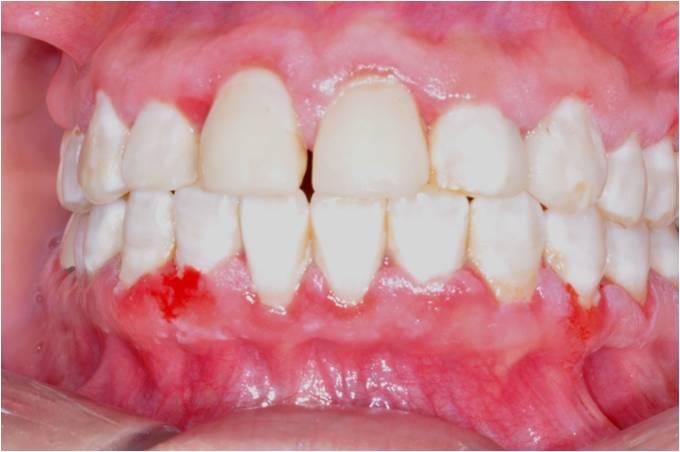
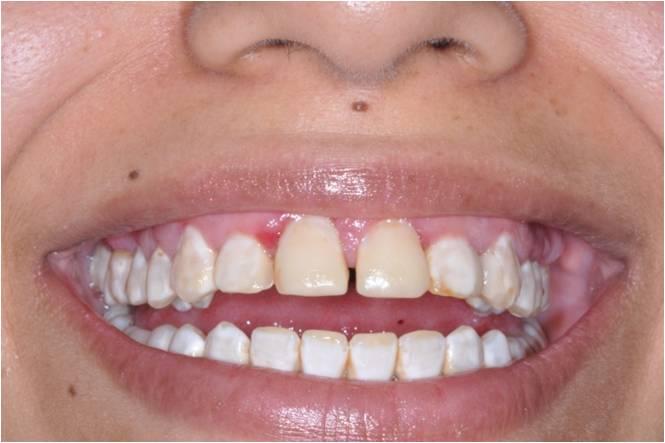
Differential Diagnosis
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
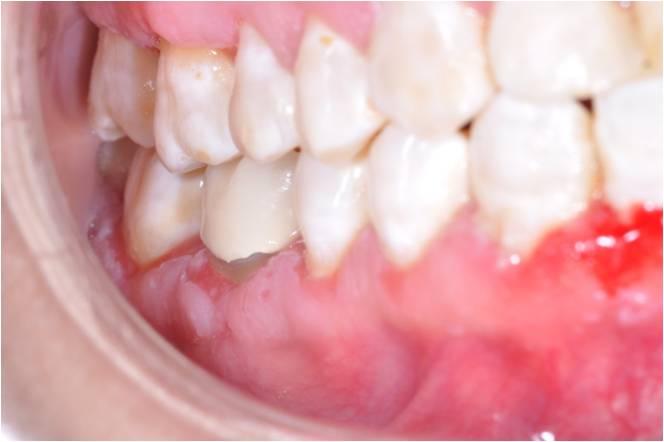
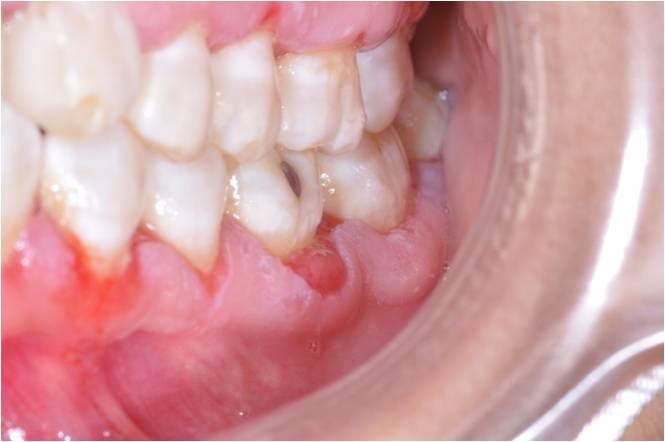
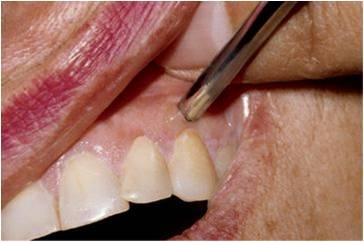
Diagnosis
Biopsy
DIF
Serum AB testing
Clinical Features
}What is the incidence and prevalence of this condition?
}0.42/100,000 in US
Mean age = 50-60 yr
}What are the systemic manifestations of this condition?
}Oral first to show last to go
}Skin
}Eyes
}Other Mucosae
}Associated w/high morbidity and significant mortality
Pathophysiology of this condition?
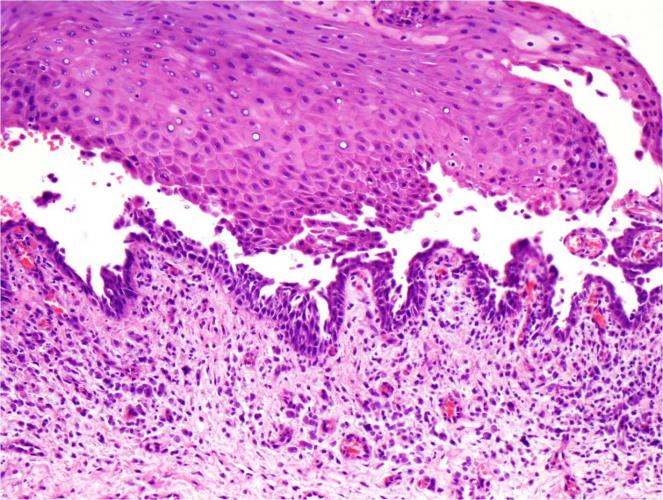
Autoantibodies, (IgG) are directed against the extracellular protein desmoglein 3 which is one of the cadherins.
Desmoglein 3 is treated as an antigen and this process produces the separation of the cells of the spinous cell layer with consequent formation of vesicles and bullae.
The process of destruction (lysis) of the intercellular connections (desmosomes) of the epithelial cells is known as acantholysis.
The union between epithelium and connective tissue is not affected in PV.
Treatment & Prognosis
Results form serum testing
Desmolgein 1 = 58 (positive >20)
Desmoglein 3 = 133 (positive >20)
PNP = negative
What is the pharmacologic treatment of PV?
Oral Agents
Dapsone = Systemic Corticosteroid
Methotrexate = Immunosupressive agent
Mycophenolate mofetil = chemotherapeutic agent which inhibits lymphocyte proliferation
Chlorambucil = alkylating immunosuppressant effecting B cells
Rituximab therapy =new therapy-chimeric monoclonal AB targeting B-cell differentiation Ag CD20
Eliminate CD20+B cells while suppressing T-cell blocks both humoral & cell mediated components of PV
Plasmapheresis =removal of AB in plasma thru filtration
IV -Ig Therapy- Newest therapy, less side effects, but fewer clinical trials
Problems with long term steroid use:
Patients on systemic steroids should maintain adequate vitamin D and calcium intake through diet and supplements. Patients with a history of renal calculi should not receive calcium carbonate.
Patients receiving long-term systemic corticosteroids should be evaluated by a rheumatologist within the first 30 days of treatment for osteoporosis risk assessment and consideration of a bisphosphonate for prophylaxis against osteoporosis.
Discussion
Pemphigus Vulgaris:
What is the dental management of this patients condition and how might your dental treatment be altered by her condition?
Prednisone short term
Dexamethasone elixir
Lidex gel
Good OH
Be careful not to traumatize
Who should you refer this patient to for medical management?
Management of patients with PV requires coordination of care between the dermatologist/rheumatologist, the patient's primary care physician & the dentist.
An ophthalmologist should evaluate patients with suspected ocular involvement and those requiring prolonged high-dose steroids.
Patients with oral disease require a dentist for evaluation and care.
References
Shih Wei Yeh,1 Naveed Sami1,2 and Razzaque A. Ahmed. Am J Clin Dermatol 2005; 6 (5): 327-342 1175-0561
Neville, Brad. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, 3rd Edition
D. Sirois, J. E. Leigh & T P. Sollecito. Oral pemphigus vulgaris preceding cutaneous lesions: Recognition and diagnosis. JADA, Vol. 131, August 2000